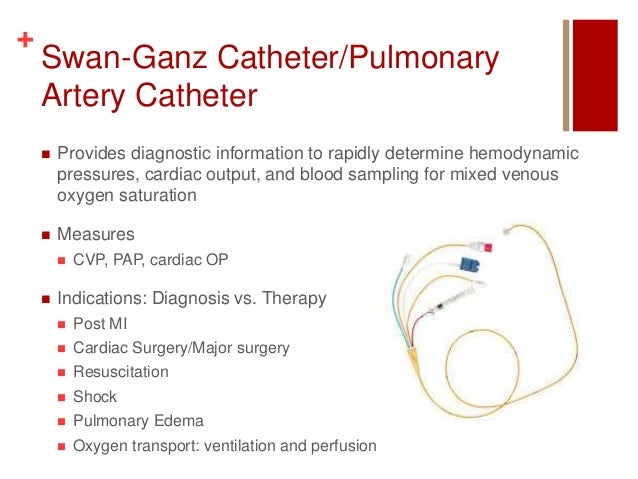
Swan Ganz Hemodynamic Monitoring. Swan ganz lines pa lines. As a result more complete hemodynamic assessment could be carried out with relative ease at the patient s bedside. Interpreting hemodynamic parameters requires both knowledge and practical experience. Recruited into stressed volume by what is termed a decrease in capacitance 10 14 a decrease in capacitance increases the upstream venous pressure and thereby in creases venous return.
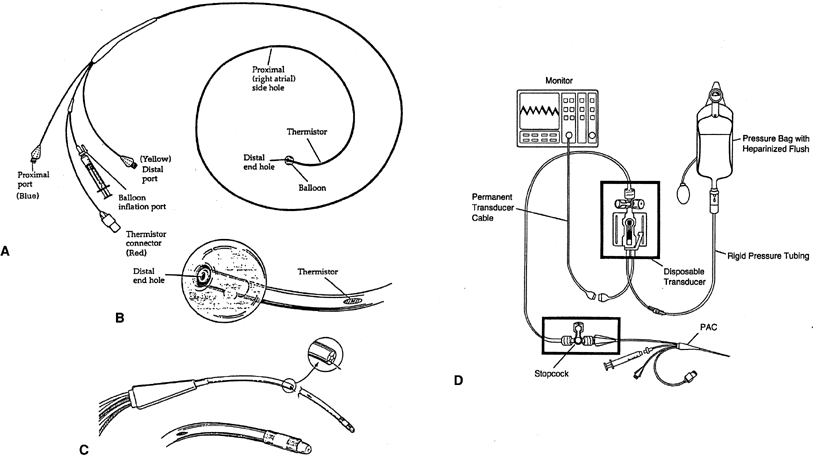
The advanced technology swan ganz catheter using the same functionality as the standard swan ganz catheter provides the ability to continuously monitor the balance between oxygen delivery and consumption and investigate the root cause of an imbalance through analysis of the components of stroke volume preload afterload and contractility. Monitoring with a pulmonary artery swan ganz catheter. As emergency nurses care for more acutely ill patients during longer ed stays an understanding of hemodynamic monitoring will be essential. The swan ganz catheter sits in the pulmonary vasculature to provide pulmonary readings which gives a reading of the ventricular function. Interpreting hemodynamic parameters requires. Invasive hemodynamic monitoring 69.
The advanced technology swan ganz catheter using the same functionality as the standard swan ganz catheter provides the ability to continuously monitor the balance between oxygen delivery and consumption and investigate the root cause of an imbalance through analysis of the components of stroke volume preload afterload and contractility.
Pulmonary artery wedge pressure. Interpreting hemodynamic parameters requires both knowledge and practical experience. Cardiac output is better expressed as the cardiac index cardiac output litres min divided by body surface area m2 which relates the cardiac output to the size of the patient. These measurements prove particularly important in patients at high risk for hemodynamic instability e g. Note that the swan ganz catheter used for hemodyanamic monitoring does not treat the patient. Monitoring pap and cardiac output in critically ill patients has been shown to provide cardiovascular information that is more accurate than that obtained by clinical assessment.