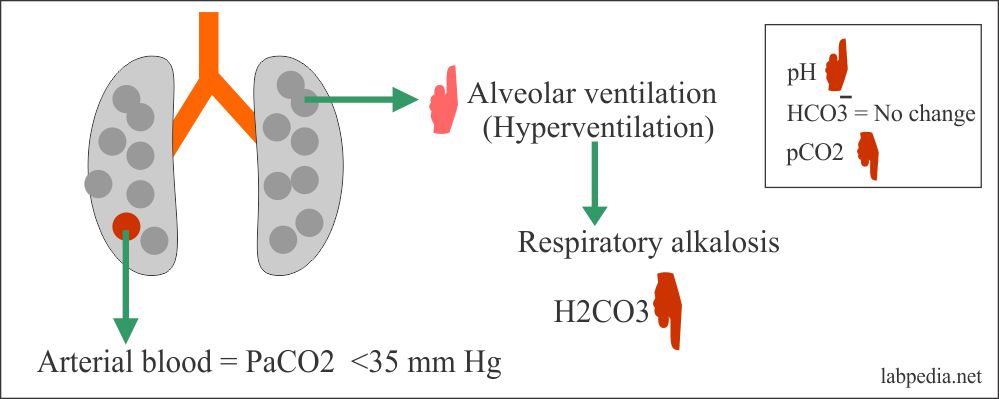
Respiratory Alkalosis Ph. Normally the respiratory system keeps these two gases in balance. You might also hear the low co 2 level referred to as hypocapnia. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. Respiratory alkalosis is a medical condition in which increased respiration elevates the blood ph beyond the normal range 7 35 7 45 with a concurrent reduction in arterial levels of carbon dioxide.
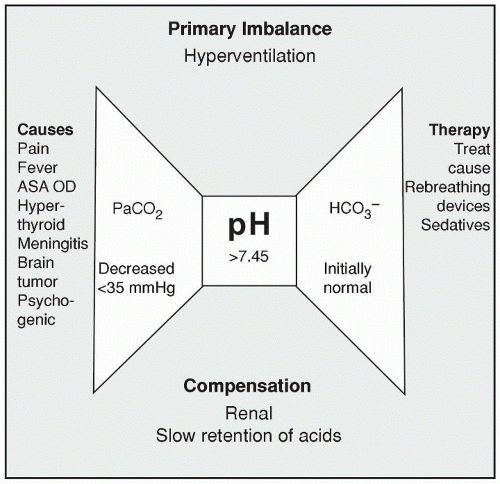
Respiratory alkalosis is a medical condition in which increased respiration elevates the blood ph beyond the normal range 7 35 7 45 with a concurrent reduction in arterial levels of carbon dioxide. A person with respiratory alkalosis will have a ph higher than 7 45 and a lower arterial carbon dioxide level because they are breathing off excess carbon dioxide. This causes the ph of. A blood sample to test for ph and arterial blood gases can be used to confirm the diagnosis. In chronic respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic.
Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic.
A person with respiratory alkalosis will have a ph higher than 7 45 and a lower arterial carbon dioxide level because they are breathing off excess carbon dioxide. Normally the respiratory system keeps these two gases in balance. A blood sample to test for ph and arterial blood gases can be used to confirm the diagnosis. Respiratory alkalosis is caused by a process whereby the ph rises in response to a decreasing pco 2. In this type of alkalosis the ph will be elevated above 7 44. In chronic respiratory alkalosis.