
Intrinsic Acute Kidney Injury. Intrinsic acute kidney injury 35 of cases intrinsic causes include any disease that leads to severe direct kidney damage. In intrinsic acute kidney injury there is structural kidney damage that can be the consequence of primary kidney disease a complication of another disease in a distant organ drug toxicity or prolonged hypo perfusion. Diseases that cause intrinsic injury to the kidney proper glomeruli tubules interstitium small blood vessels are grouped under renal causes or intrinsic causes e g acute glomerulonephritis acute tubular necrosis acute interstitial nephritis or small vessel vasculitis. Acute kidney injury aki in the intensive care unit icu can be the result of a wide range of disease processes so that it is likely to be encountered by physicians from all specialties.
Most commonly caused by sepsis infection ischemia and or nephrotoxins. Intrinsic renal causes of acute kidney injury are categorized by the location of the injury most commonly the glomerulus or tubule and include the interstitial or vascular portions of the kidney. Once hemodynamic and postrenal causes of aki have been excluded acute renal dysfunction that is intrinsic to the kidneys must be considered. Aki is diagnosed on the basis of characteristic laboratory findings such as ele. Glomerulonephritis e g rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis vascular. Intrinsic renal causes are also important sources of acute kidney injury and can be categorized by the component of the kidney that is primarily affected i e tubular glomerular interstitial.
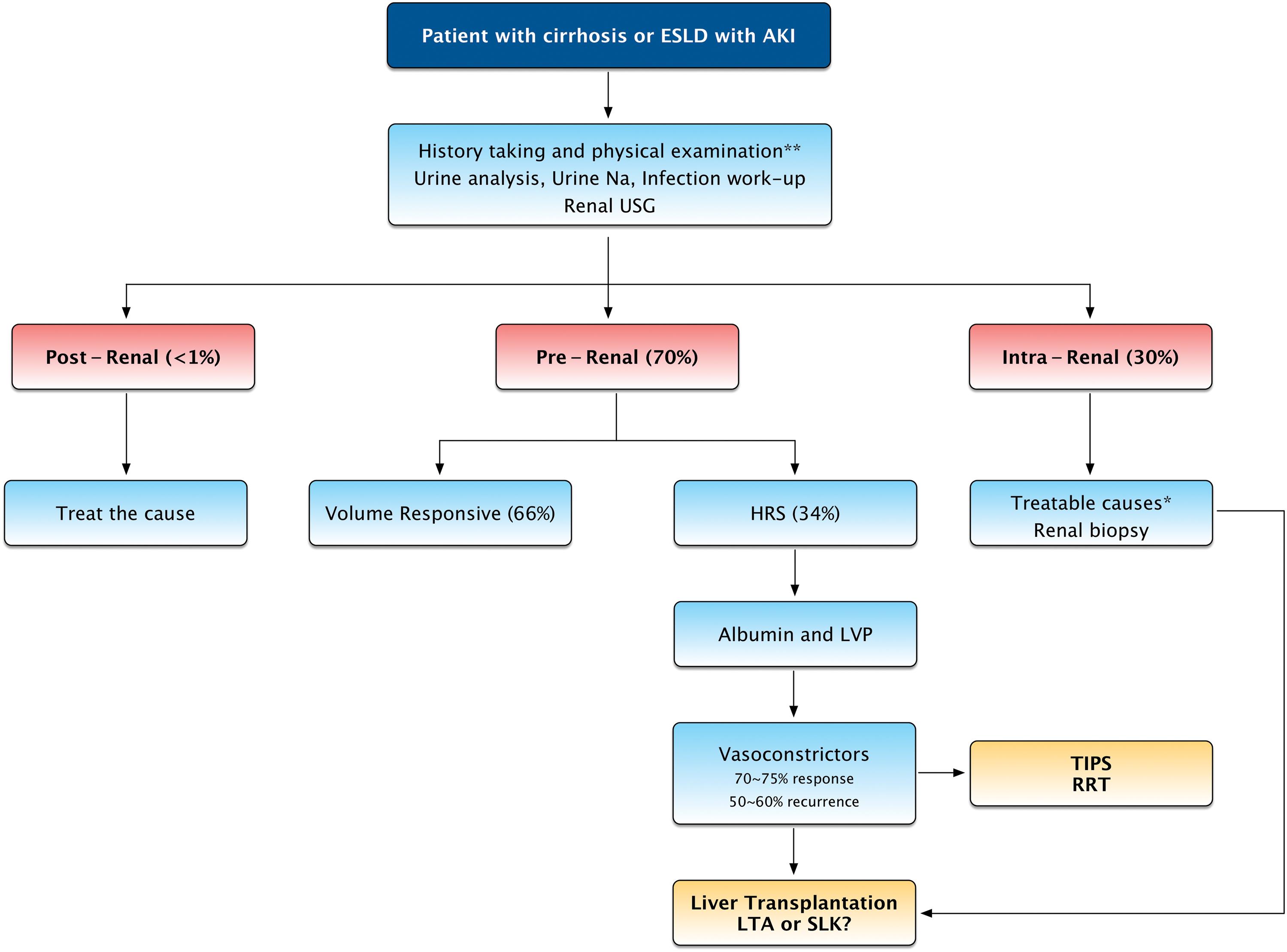
The most common cause of acute kidney injury aki is acute tubular necrosis atn when the pattern of injury lies within the kidney intrinsic disease.
Generally it occurs because of damage to the kidney tissue caused by decreased kidney blood flow from any cause exposure to substances harmful to the kidney an inflammatory process in the kidney or an obstruction of the urinary tract that impedes the flow of urine. Acute kidney failure also called acute renal failure or acute kidney injury develops rapidly usually in less than a few days. Intrinsic acute kidney injury 35 of cases intrinsic causes include any disease that leads to severe direct kidney damage. The approach to intrinsic renal injury varies according to the affected part of the kidney. Once hemodynamic and postrenal causes of aki have been excluded acute renal dysfunction that is intrinsic to the kidneys must be considered. Intrinsic renal causes are also important sources of acute kidney injury and can be categorized by the component of the kidney that is primarily affected i e tubular glomerular interstitial.