
Acid Base Balance Compensation. It is faster than renal compensation but has less ability to restore normal values in the case of metabolic acidosis chemoreceptors sense a deranged acid base system and there is increased breathing 6. Sbe is normal no metabolic compensation. Ph 7 2 pco 2 60 mmhg 8 kpa sbe 0 meq l. Overall change is acid.
Overall change is acid. Respiratory change is also acid therefore contributing to the acidosis. This leads to an increase in rr and or tv which leads to increased exhalation of co 2 p a co 2 1 2 x δhco 3. Hypoxia can increase the amount of peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation. When both components are acid this is not a typical single condition but a combined metabolic and respiratory acidosis. The limit of compensation is a pco2 of about 10 mmhg.
When ph a arterial blood ph differs from 7 4 0 02 or the h differs from 40 2 neq l there occurs acidemia ph a 7 38 h 42 neq l or alkalemia ph a 7 42 h 38 neq l.
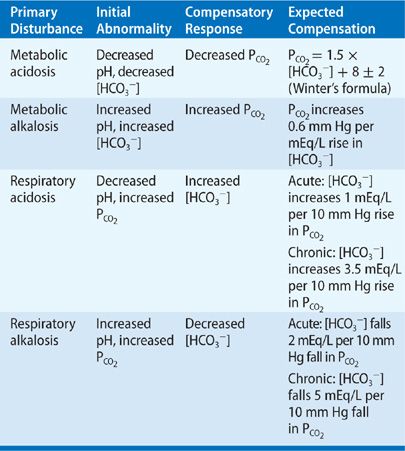
When both components are acid this is not a typical single condition but a combined metabolic and respiratory acidosis. Most investigators striving to typify compensations for abnormal acid base balance have reported their findings in terms of arterial ph paco2 and or hco3. Renal and respiratory acid base regulation systems interact with each other one compensating partially for a primary defect of the other. The limit of compensation is a pco2 of about 10 mmhg. A decrease in ph within the arteries and csf leads to increased stimulation of the medullary chemoreceptors. If the ph a change is due primarily to a change in p aco2 there is respiratory acidosis p aco2 42 mmhg or respiratory alkalosis p aco2 38.